Collection: NIACIN
Niacin (Vitamin B3) Overview:
Niacin, also known as vitamin B3, is an essential water-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in converting food into energy. It helps maintain the health of your nervous system, digestive system, and skin. Niacin is found naturally in foods like meat, fish, nuts, seeds, and grains, and can also be taken as a supplement for various health benefits.
Forms of Niacin:
- Nicotinic Acid: The most common form, often used to improve cholesterol levels.
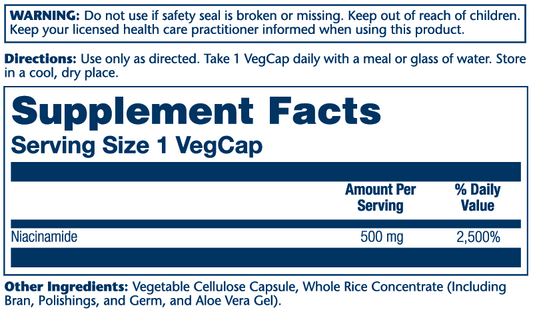
- Niacinamide (Nicotinamide): A form of niacin used primarily in skincare and for its anti-inflammatory properties.
Benefits of Niacin:
- Cholesterol Management: Niacin can increase good HDL cholesterol and lower triglycerides, which is why it's often prescribed for those with high cholesterol. It also has a mild effect on lowering bad LDL cholesterol.
- Energy Production: Niacin is vital for the body to convert food into energy by aiding in cellular metabolism.
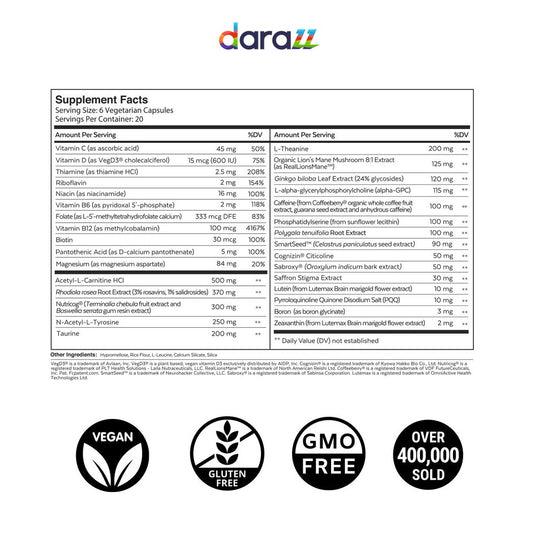
- Skin Health: Niacinamide, a form of niacin, is commonly used in skincare products due to its anti-inflammatory and anti-acne properties.
- Brain Function: It may help improve cognitive function, slow memory loss, and protect against dementia in some cases.
- DNA Repair: Niacin plays a role in the synthesis and repair of DNA, contributing to overall cellular health.
Niacin for Cholesterol:
Niacin is often prescribed at higher doses to treat high cholesterol. It can raise HDL cholesterol, which helps remove LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream. However, high doses can cause side effects, including liver damage, gastrointestinal issues, and glucose intolerance. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional before using niacin for cholesterol management.
Recommended Dosage:
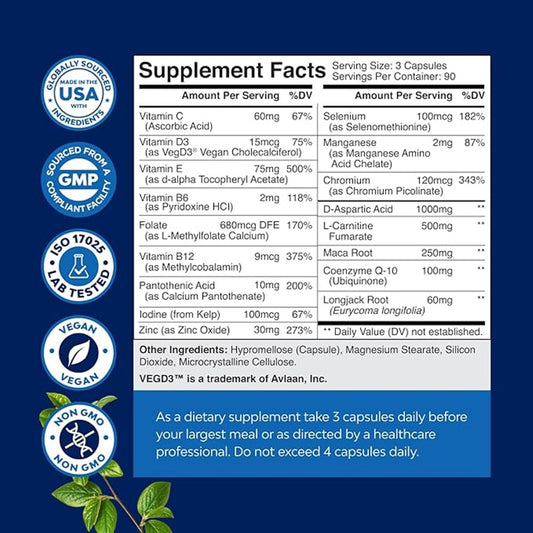
- Adults: 16 mg/day for men and 14 mg/day for women.
- Pregnant Women: 18 mg/day.
- Lactating Women: 17 mg/day.
- Upper Limit: The maximum recommended dose for niacin is 35 mg/day for adults to avoid adverse effects.
Forms Available:
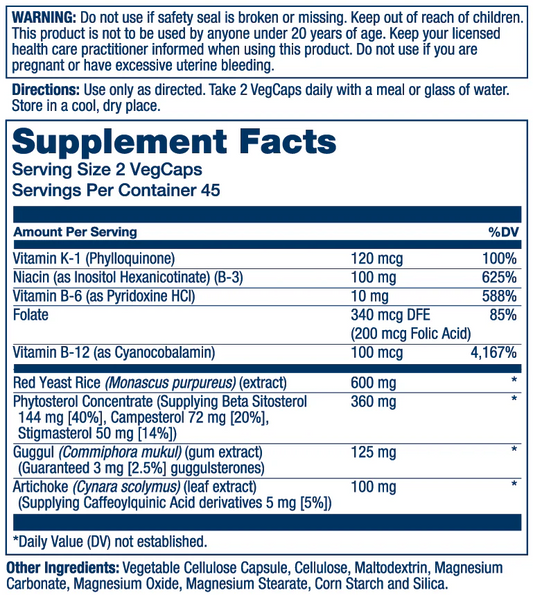
- Tablets and Capsules: Available in various dosages (e.g., 500 mg, 1000 mg, 250 mg) for specific health needs.
- Extended/Slow Release: These forms are designed to release niacin gradually, reducing the likelihood of side effects like the niacin flush.
- Niacinamide Supplements: Often used in skincare and for its anti-inflammatory effects.
- Powder: A versatile form of niacin, which can be used in various formulations.
Niacin Flush:
Niacin flush is a temporary side effect characterized by redness, warmth, or itching of the skin, often caused by higher doses of niacin. No-flush niacin supplements are available for those who want to avoid this side effect.
Niacinamide vs. Niacin:
While both are forms of vitamin B3, niacinamide (nicotinamide) is often used in skincare products to treat acne, while niacin (nicotinic acid) is commonly used for cholesterol management.
Niacin in Supplements:
Niacin is available in various forms such as tablets, capsules, powders, and extended-release formulations. The supplements come in different dosages, including 50 mg, 100 mg, 250 mg, 500 mg, and 1000 mg, with slow-release and no-flush options for different needs.
Safety Considerations:
- Excess Niacin: Taking high doses of niacin (especially without medical supervision) can lead to serious side effects, including liver damage and gastrointestinal issues.
- Consultation with a Healthcare Professional: It's recommended to seek medical advice before using niacin for cholesterol management or other health conditions.
Conclusion:
Niacin is an essential vitamin with a wide range of benefits, from supporting energy metabolism to improving cholesterol levels and skin health. Whether you're considering niacin for general health, cholesterol management, or skincare, it's important to choose the right form and dosage for your needs. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting high-dose niacin supplements to ensure safe and effective use.
-
Qualia Mind™ - Premium Cognitive Support | Focus, Memory & Drive | 154 Capsules
Regular price Rs.8,599.00 PKRRegular priceUnit price / perRs.9,500.00 PKRSale price Rs.8,599.00 PKRSale -
Nature's Craft Male Fertility Support - Formula for Male Reproductive Health
Regular price From Rs.7,500.00 PKRRegular priceUnit price / per -
LIFE EXTENSION Vitamin B3 (Niacin) 500mg – Supports Cardiovascular Health | 100 Vegan Capsules
Regular price Rs.4,999.00 PKRRegular priceUnit price / perRs.6,000.00 PKRSale price Rs.4,999.00 PKRSale -
NOW Niacin 500mg – Vitamin B3 Supplement for Nutritional Health | 100 Vegan Capsules
Regular price Rs.4,999.00 PKRRegular priceUnit price / perRs.6,000.00 PKRSale price Rs.4,999.00 PKRSale -
The Ordinary Niacinamide 10% + Zinc 1% Pore Minimizing Serum.
Regular price Rs.3,000.00 PKRRegular priceUnit price / perRs.2,799.00 PKRSale price Rs.3,000.00 PKR -
Dorado Nutrition Blood Circulation 150 Capsules
Regular price Rs.5,638.22 PKRRegular priceUnit price / perRs.5,980.00 PKRSale price Rs.5,638.22 PKRSale -
Now Foods Niacinamide 1000 Mg – Energy & Skin Health – 90 Tablets
Regular price Rs.4,890.00 PKRRegular priceUnit price / perRs.5,120.00 PKRSale price Rs.4,890.00 PKRSale -
Advanced Trichology NutraM Hair Growth Serum
Regular price Rs.3,000.00 PKRRegular priceUnit price / perRs.2,899.00 PKRSale price Rs.3,000.00 PKR -
Bake 2% Alpha Arbutin Face Serum with Kojic Acid & Niacinamide
Regular price Rs.3,499.00 PKRRegular priceUnit price / perRs.4,000.00 PKRSale price Rs.3,499.00 PKRSale -
Top Nutrition Thermo Smash Strawberry 350g
Regular price Rs.16,125.93 PKRRegular priceUnit price / perRs.16,889.00 PKRSale price Rs.16,125.93 PKRSale -
Solaray Cardio Complete, Cardiovascular 90 Caps
Regular price Rs.4,800.00 PKRRegular priceUnit price / perRs.4,900.00 PKRSale price Rs.4,800.00 PKRSale -
Solaray Niacin, No Flush 500mg 100 Caps
Regular price Rs.9,258.71 PKRRegular priceUnit price / perRs.9,450.00 PKRSale price Rs.9,258.71 PKRSale -
Solaray Niacin 100mg 100 Caps
Regular price Rs.2,967.61 PKRRegular priceUnit price / perRs.3,120.00 PKRSale price Rs.2,967.61 PKRSale -
Solaray Niacin 500mg 100 Caps
Regular price Rs.3,831.22 PKRRegular priceUnit price / perRs.4,120.00 PKRSale price Rs.3,831.22 PKRSale -
Solaray Niacinamide 500mg 100 Caps
Regular price Rs.3,972.19 PKRRegular priceUnit price / perRs.4,120.00 PKRSale price Rs.3,972.19 PKRSale -
Bronson Vitamins No Flush Niacinamide Vitamin B3 - 500 Mg - 250 Tablets
Regular price Rs.3,500.00 PKRRegular priceUnit price / perRs.3,600.00 PKRSale price Rs.3,500.00 PKRSale -
Bluebonnet Nutrition Flush-Free Niacin 500 Mg 60 Caps
Regular price Rs.3,800.00 PKRRegular priceUnit price / perRs.3,900.00 PKRSale price Rs.3,800.00 PKRSale -
Bluebonnet Nutrition Niacinamide 500 Mg 60 Caps
Regular price Rs.3,800.00 PKRRegular priceUnit price / perRs.3,900.00 PKRSale price Rs.3,800.00 PKRSale -
Bluebonnet Nutrition Niacin 100 Mg 90 Caps
Regular price Rs.4,800.00 PKRRegular priceUnit price / perRs.4,900.00 PKRSale price Rs.4,800.00 PKRSale -
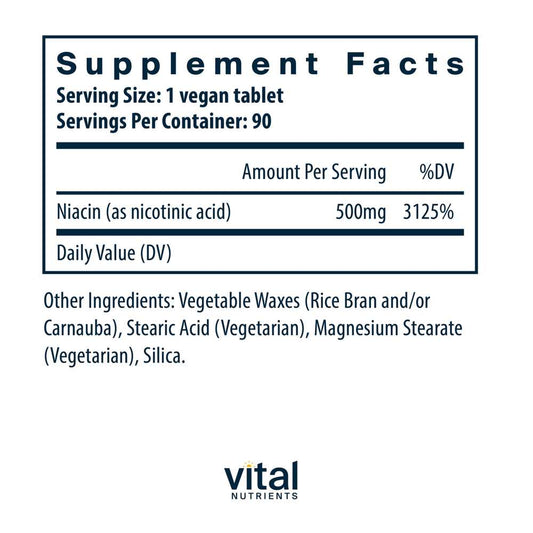
Vital Nutrients Niacin 500mg 90 Tabs
Regular price Rs.4,800.00 PKRRegular priceUnit price / perRs.4,900.00 PKRSale price Rs.4,800.00 PKRSale
Couldn't Find Your Answer?
If you couldn't find the answer you're looking for, our team is here to assist you. Feel free to reach out, and we'll be happy to help!